Egg freezing, or oocyte cryopreservation, has become an increasingly popular option for individuals seeking to preserve fertility. Once considered experimental, it is now widely accessible and marketed as a solution for those who wish to delay parenthood. But what are the actual benefits and limitations of egg freezing? Here’s a closer look at the science, costs, and considerations behind this life-changing decision.
How Egg Freezing Works
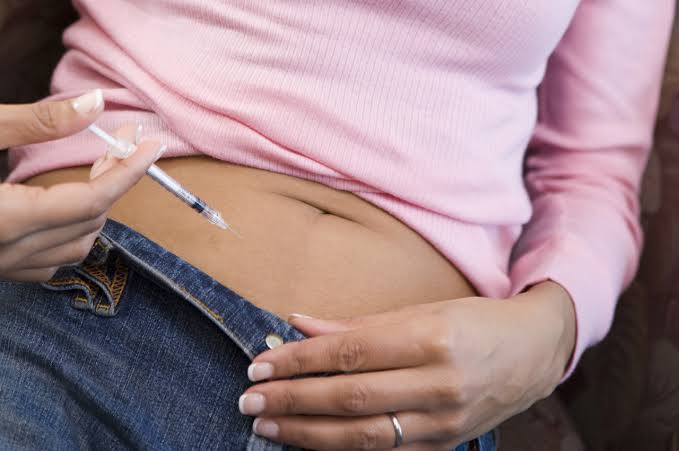
Egg freezing involves stimulating the ovaries with hormones to produce multiple eggs, which are then retrieved and flash-frozen using a technique called vitrification. The eggs can later be thawed, fertilized with sperm, and implanted as embryos through in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Who Should Consider Egg Freezing?
Egg freezing is often recommended for individuals in the following situations:
- Career or Education Goals: Those who want to delay parenthood but are concerned about age-related fertility decline.
- Medical Reasons: People undergoing treatments like chemotherapy, which can impair fertility.
- Personal Circumstances: Those without a partner or in situations where childbearing might not be immediately feasible.
Benefits of Egg Freezing
- Preservation of Fertility: Egg freezing can offer a sense of control by extending the window of reproductive opportunity.
- Improved Technology: Advances in vitrification have significantly increased egg survival rates and pregnancy success rates.
- Emotional Reassurance: For many, freezing eggs alleviates anxiety about the biological clock and provides a backup plan.
Limitations and Realities
- Success Rates Vary: While freezing technology has improved, not all frozen eggs result in pregnancies. Factors like age at freezing and overall egg quality play a critical role. For example:
- Women under 35 typically have better outcomes.
- Women over 38 may freeze eggs with lower viability, making success less likely.
- It’s Not a Guarantee: Even with egg freezing, there’s no certainty of achieving a live birth in the future.
- High Costs: The procedure can cost $6,000 to $15,000 per cycle, excluding medication, storage fees, and future IVF costs. Multiple cycles may be necessary to retrieve a sufficient number of eggs.
- Physical and Emotional Toll: The process involves hormone injections, medical appointments, and potential side effects like bloating, mood swings, and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS).
- Storage and Longevity: Eggs can be stored for years, but longer storage periods may pose slight risks to egg quality.
Social and Ethical Considerations
- Marketing and Misconceptions: Some critics argue that clinics overpromise success rates, leading individuals to overestimate their chances of future pregnancies.
- Pressure to Delay Parenthood: Egg freezing may inadvertently reinforce societal pressures that prioritize career over family planning, leaving individuals to navigate complex personal decisions.
Egg Freezing by the Numbers
- Women who freeze eggs before age 35 have a 70-90% chance of a live birth from 10-20 eggs.
- For women over 40, the likelihood drops to less than 10% per egg.
- Around 10% of those who freeze their eggs eventually return to use them, according to some studies.
Is Egg Freezing Right for You?
The decision to freeze eggs is deeply personal and depends on factors like age, health, financial situation, and long-term goals. Consulting with a fertility specialist can help provide a clearer picture of individual success rates and what to expect.
What do you think about egg freezing? Would you love to try it?

![[Galaxy Unpacked 2025] A First Look At The Galaxy Z Fold7](https://www.techquery.ng/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/EC5C9262-C536-4F53-BAB3-5B53771FD5F6-183x150.png)